Health
First Documented Death from Alpha-Gal Syndrome Highlights Risks
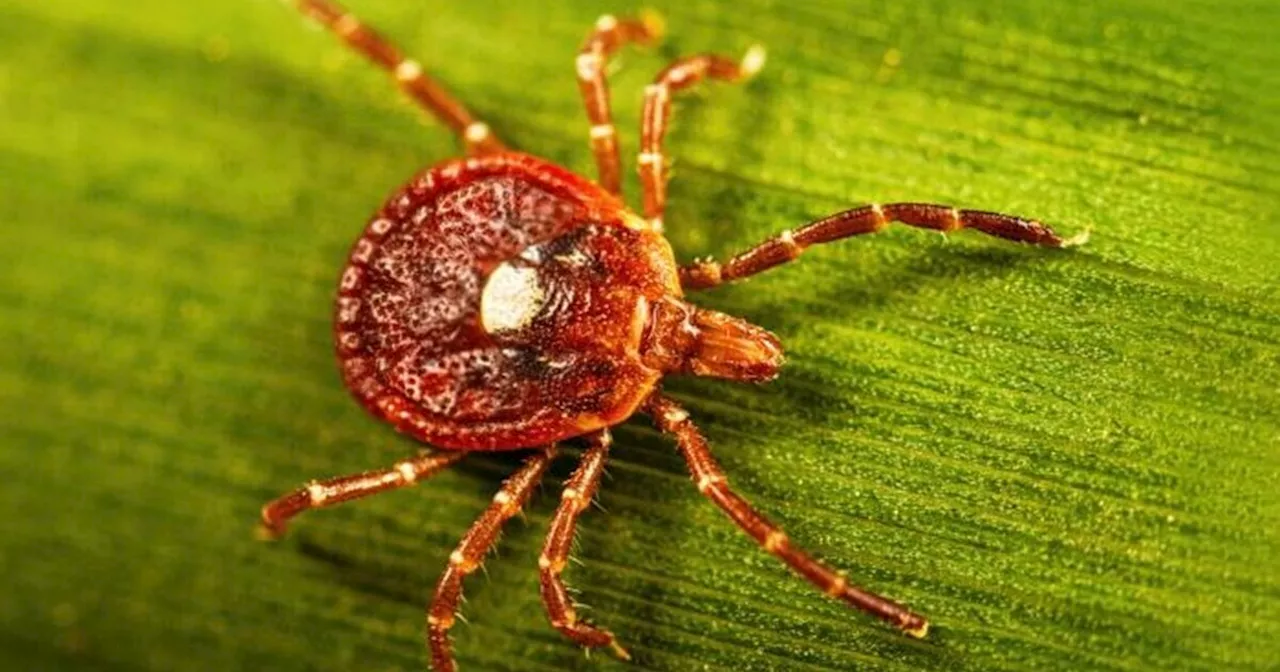

Researchers have reported the first documented death related to *alpha-gal syndrome*, a severe allergy to red meat triggered by bites from the lone star tick. The tragic case involves a 47-year-old pilot from New Jersey who died after consuming a hamburger during a barbecue in 2024. This incident emphasizes the potentially life-threatening nature of the allergy and raises alarms about the increasing prevalence of tick-borne illnesses.
The findings were published in a report from the *University of Virginia School of Medicine*, detailing the events leading to the pilot’s death. Approximately four hours after eating, he fell ill and was found unconscious in a bathroom. Despite immediate medical intervention, he was pronounced dead at a hospital. The autopsy attributed the death to a sudden unexplained event, underscoring the unexpected severity of alpha-gal syndrome.
The pilot’s wife disclosed that he had previously experienced adverse reactions after consuming red meat, including abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. These symptoms were often misinterpreted as food poisoning, illustrating the difficulties in recognizing and diagnosing the syndrome. Prior to the fatal incident, he had reported similar symptoms after eating steak but had not sought medical attention.
Further investigations revealed that the pilot had sustained multiple bites from lone star ticks, known to transmit alpha-gal syndrome. Initial misidentification of these bites as chigger bites may have contributed to the delayed diagnosis. The presence of *alpha-gal*, a sugar molecule found in mammals, caused his immune system to react dramatically upon the consumption of red meat, leading to a severe allergic response that ultimately resulted in his death.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (*CDC*) has highlighted a significant rise in identified cases of alpha-gal syndrome, estimating that as many as **450,000 individuals** may be affected, which far exceeds the number of confirmed diagnoses. This underlines the urgent need for increased awareness among healthcare providers and patients regarding the symptoms and risks associated with the syndrome.
Alpha-gal syndrome, characterized by an allergic reaction to the alpha-gal sugar, poses a growing public health concern, particularly due to the rising population of lone star ticks in the United States. Environmental changes, including warming temperatures and shifts in habitats, are believed to contribute to the northward migration of these ticks. This geographic expansion exposes more individuals to the risk of developing alpha-gal syndrome.
Experts recommend several preventative measures, including the use of insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding areas known to harbor ticks. If bitten, it is crucial to remove the tick promptly and save it in a plastic bag for identification. Early removal can significantly reduce the risk of infection and subsequent health complications.
Currently, there is no vaccine for alpha-gal syndrome. The primary strategy for managing the allergy involves dietary changes, notably the elimination of red meat. The pilot’s death serves as a critical reminder of the allergy’s potential severity and the necessity for early diagnosis and effective management strategies.
The findings from this case underscore the importance of raising public awareness about alpha-gal syndrome and its symptoms. As the number of cases and the distribution of lone star ticks continue to rise, it is vital to enhance understanding of the disease, its triggers, and preventive measures to protect public health effectively.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoInventor Achieves Breakthrough with 2 Billion FPS Laser Video
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoCommunity Unites for 7th Annual Into the Light Walk for Mental Health
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoCharlie Sheen’s New Romance: ‘Glowing’ with Younger Partner
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoDua Lipa Aces GCSE Spanish, Sparks Super Bowl Buzz with Fans
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoTyler Technologies Set to Reveal Q3 Earnings on October 22
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoMother Fights to Reunite with Children After Kidnapping in New Drama
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoCurium Group, PeptiDream, and PDRadiopharma Launch Key Cancer Trial
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoR&B Icon D’Angelo Dies at 51, Leaving Lasting Legacy
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoRed Sox’s Bregman to Become Free Agent; Tigers Commit to Skubal
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoNorth Carolina’s Biotech Boom: Billions in New Investments
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNorth Carolina’s Biotech Boom: Billions Invested in Manufacturing
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoYouTube Launches New Mental Health Tools for Teen Users