Science
Scientists Unveil Ancient Civilizations and Cosmic Discoveries
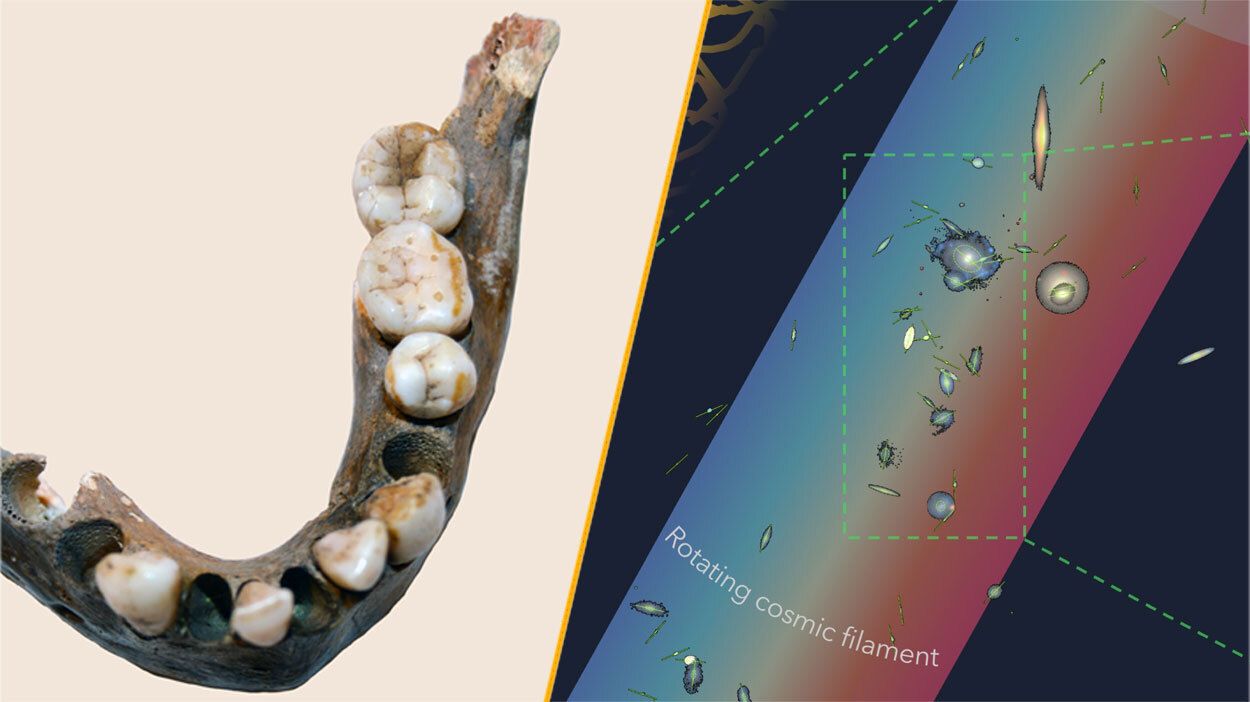
This week has brought significant developments in the world of science, highlighting discoveries that range from ancient human populations to cosmic phenomena. A team of astronomers has identified the largest spinning structure in the known universe, located approximately 140 million light-years away. Meanwhile, researchers have examined an isolated human population in southern Africa that existed for 100,000 years. These findings provide valuable insights into our planet’s history and the broader universe.
Galactic Discoveries and Evolutionary Insights
The newly discovered rotating filament, which is wider than the Milky Way, is linked to a daisy chain of 14 galaxies. It is spinning at an impressive 68 miles per second (approximately 110 kilometers per second). This remarkable finding underscores the complexity of cosmic structures and offers astronomers a unique opportunity to study the dynamics of such massive formations.
In a more terrestrial discovery, geneticists have focused their research on a human population that thrived south of the Limpopo River for tens of millennia. The study analyzed skeletons dated up to 10,000 years old, revealing that individuals who lived over 1,400 years ago exhibited a significantly different genetic profile compared to modern humans. This group represents “an extreme end of human genetic variation,” according to researchers, emphasizing the rich tapestry of human evolution.
Archaeological Findings and Environmental Concerns
In China, archaeologists have unearthed a mass grave containing skulls, predominantly of males, near a city that dates back 4,000 years. The unusual male-skewed distribution deviates from known human sacrificial patterns observed at other nearby sites, raising questions about the cultural practices of the time. Similarly, a tomb in Greece dating back 2,700 years contained a woman adorned with an upside-down crown, further intriguing researchers about ancient rituals and beliefs.
On a more contemporary note, a decades-long initiative in China known as the Great Green Wall aimed to combat desertification through extensive tree planting. Although the project has successfully expanded green cover, a recent analysis indicates it has inadvertently altered rainfall and evaporation patterns, leading to decreased water levels in some of the country’s most populous regions.
In the realm of climate anomalies, researchers are revisiting the record for the hottest temperature ever recorded on Earth, set in Death Valley in 1913. New investigations suggest that human error may have played a role in the measurement, prompting discussions about the accuracy of historical climate data. Meanwhile, scientists are warning that the collapse of a critical Atlantic current could result in prolonged drought conditions across Europe.
The interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS, which captured public interest when it entered our solar system, is now showing signs of activity that resemble “ice volcanoes.” Observations from the Joan Oró Telescope in northeastern Spain have indicated that the comet is heating up and emitting jets as it approaches the sun. This sublimation of ice suggests that 3I/ATLAS shares characteristics with other icy bodies in our solar system.
In technological advancements, engineers at MIT have developed a method to extract drinking water from the air using ultrasound technology. This innovative approach, which is 45 times more efficient than traditional evaporation methods, could provide a critical resource in arid regions. Although the device requires a power source, researchers believe it can be effectively paired with solar energy solutions.
As the scientific community continues to uncover the mysteries of our past and the cosmos, the latest findings serve to remind us of the intricate connections between humanity, the environment, and the universe. Each discovery opens new avenues for exploration and understanding, reinforcing the importance of ongoing research in these diverse fields.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoInventor Achieves Breakthrough with 2 Billion FPS Laser Video
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoCommunity Unites for 7th Annual Into the Light Walk for Mental Health
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoCharlie Sheen’s New Romance: ‘Glowing’ with Younger Partner
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoDua Lipa Aces GCSE Spanish, Sparks Super Bowl Buzz with Fans
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoCurium Group, PeptiDream, and PDRadiopharma Launch Key Cancer Trial
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoMother Fights to Reunite with Children After Kidnapping in New Drama
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoFormer Mozilla CMO Launches AI-Driven Cannabis Cocktail Brand Fast
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoIsrael Reopens Rafah Crossing After Hostage Remains Returned
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoTyler Technologies Set to Reveal Q3 Earnings on October 22
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNorth Carolina’s Biotech Boom: Billions in New Investments
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoR&B Icon D’Angelo Dies at 51, Leaving Lasting Legacy
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoRed Sox’s Bregman to Become Free Agent; Tigers Commit to Skubal









