Science
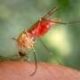
Biodiversity Loss Fuels Surge in Mosquito Populations in Brazil

The ongoing decline in biodiversity is contributing to an alarming increase in mosquito populations in the Atlantic Forest of Brazil. As human activities continue to encroach on this vital ecosystem, only about one-third of its original area remains intact, leading to significant ecological imbalance.
The Atlantic Forest stretches along the eastern coast of Brazil and is home to a diverse array of wildlife, including hundreds of species of birds, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and fishes. According to a study published in the journal *Nature Ecology & Evolution* in 2023, the reduction of this habitat has intensified the thirst of mosquitoes for human blood.
Human expansion, driven by urbanization and agriculture, has carved into the forest, displacing wildlife and disrupting natural ecosystems. The loss of biodiversity is not only an environmental issue but also a public health concern. Mosquitoes, which thrive in disturbed habitats, are becoming more prevalent as they adapt to the changing landscape.
Impact on Public Health
The increase in mosquito populations poses a greater risk for the transmission of diseases such as dengue fever, Zika virus, and chikungunya. As these insects become more abundant and aggressive, the likelihood of human interaction rises, creating a concerning public health scenario.
Dr. Maria Elena Bottazzi, a prominent researcher in tropical medicine, emphasized the importance of preserving biodiversity to mitigate such health risks. She stated, “By maintaining healthy ecosystems, we can reduce the conditions that allow mosquitoes to thrive.” This sentiment underscores the interconnectedness of biodiversity and human health.
In recent years, Brazilian authorities have implemented various measures to combat mosquito-borne diseases. These include public awareness campaigns and vector control programs aimed at reducing mosquito populations. However, the underlying issue of habitat destruction remains unaddressed, as urban sprawl continues to threaten the Atlantic Forest.
Conservation Efforts and Future Outlook
Conservation groups are advocating for stronger measures to protect the remaining portions of the Atlantic Forest. Initiatives include reforestation projects and the establishment of protected areas to preserve biodiversity and help restore ecological balance.
The Brazilian government, alongside international organizations, is exploring sustainable development practices that can coexist with environmental preservation. As of 2023, it is estimated that approximately 60% of the original Atlantic Forest has been lost, highlighting the urgency of these conservation efforts.
The implications of biodiversity loss extend beyond mosquitoes. A healthy and diverse ecosystem supports various species and contributes to the overall resilience of the environment. As the situation evolves, it is crucial for stakeholders to prioritize ecological health to safeguard both wildlife and human populations.
In summary, the increasing mosquito populations in Brazil’s Atlantic Forest serve as a stark reminder of the consequences of biodiversity loss. Without concerted efforts to protect and restore this vital habitat, the risks to public health and the environment will continue to grow. The time to act is now, not just for the forest, but for the well-being of communities that depend on it.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoInventor Achieves Breakthrough with 2 Billion FPS Laser Video
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoCommunity Unites for 7th Annual Into the Light Walk for Mental Health
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoCharlie Sheen’s New Romance: ‘Glowing’ with Younger Partner
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoDua Lipa Aces GCSE Spanish, Sparks Super Bowl Buzz with Fans
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMother Fights to Reunite with Children After Kidnapping in New Drama
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoResearchers Launch $1.25M Project for Real-Time Hazard Monitoring in Hawaiʻi
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoFormer Mozilla CMO Launches AI-Driven Cannabis Cocktail Brand Fast
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoR&B Icon D’Angelo Dies at 51, Leaving Lasting Legacy
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoParenting Pitfalls: 16 Small Mistakes with Long-Term Effects
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoCurium Group, PeptiDream, and PDRadiopharma Launch Key Cancer Trial
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoAI Gun Detection System Mistakes Doritos for Weapon, Sparks Outrage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoOlivia Plath Opens Up About Her Marriage Struggles and Divorce