Science
New Study Indicates Universe Is Slowing Down Expansion Rate
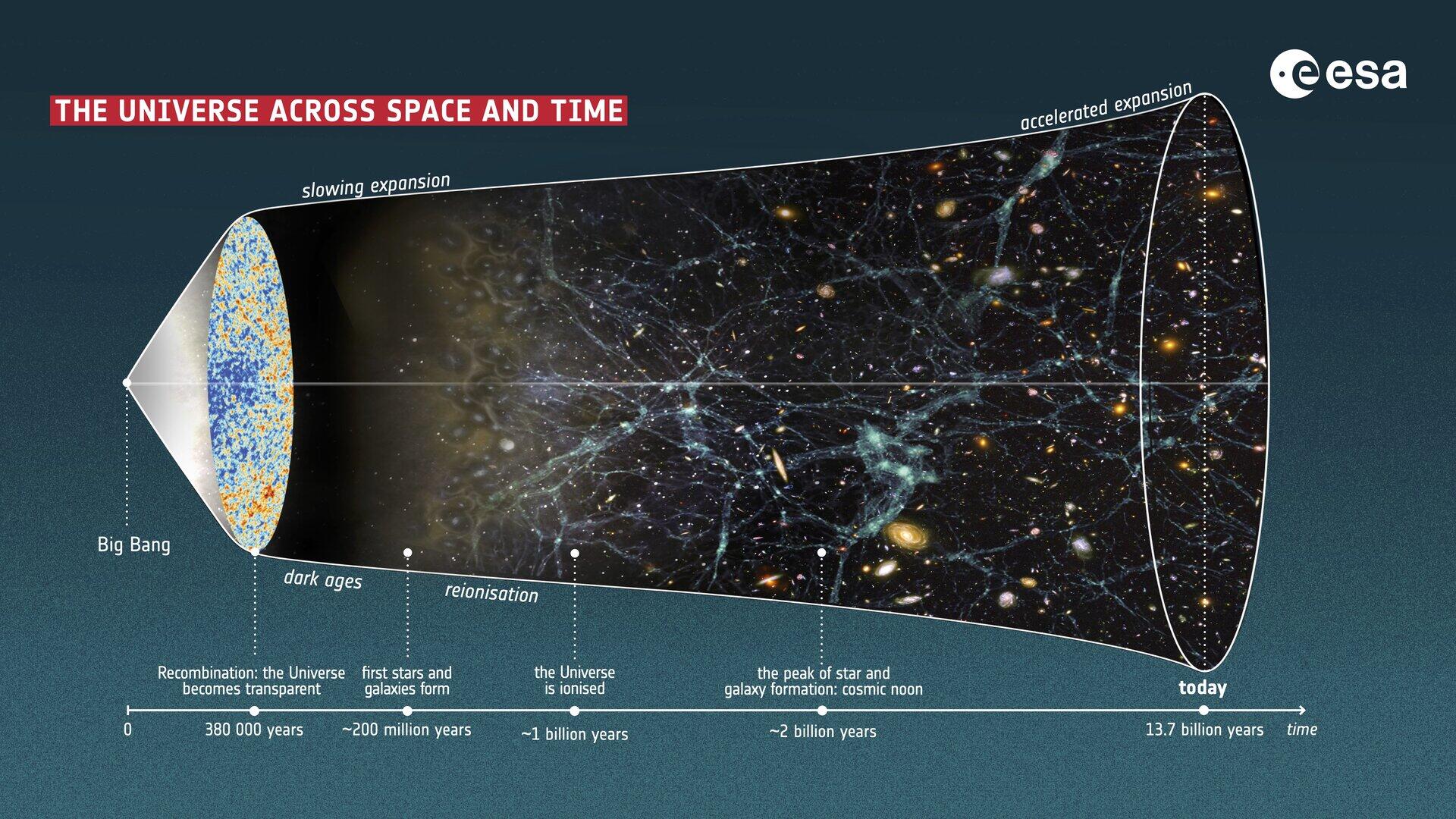
A recent study led by Professor Young-Wook Lee from Yonsei University in South Korea suggests that the universe is currently experiencing a slowdown in its expansion. The findings challenge long-held beliefs about the behavior of dark energy, which has been thought to drive the accelerating expansion of the cosmos. The research provides strong statistical evidence supporting this decelerated phase at the present epoch.
The concept of a “Hubble residual” is central to this study, as it tracks the age of the universe’s host with significant statistical backing. According to Professor Lee, “Our study shows that the universe has already entered a phase of decelerated expansion at the present epoch and that dark energy evolves with time much more rapidly than previously thought.” This statement emphasizes the potential implications of the research, which could lead to a fundamental shift in cosmological understanding.
Implications for Cosmology
If these findings are confirmed through further research, they could signify a major paradigm shift in cosmology, marking the first significant change in understanding dark energy since its discovery approximately 27 years ago. The implications extend beyond theoretical physics, prompting a reevaluation of existing models that describe the universe’s expansion and the forces that govern it.
The study’s results align with growing skepticism within the scientific community regarding the nature of dark energy. While previous models posited a consistent acceleration, this new evidence suggests a more complex relationship that could redefine how scientists approach cosmological research.
The research also highlights the importance of ongoing observation and analysis in astronomy. Understanding the universe’s expansion is crucial not only for theoretical physics but also for grasping the larger narrative of cosmic evolution.
As this investigation develops, the scientific community will likely scrutinize the methodology and data presented by Lee and his team. Continued exploration into dark energy may provide further insights into how the universe operates, reshaping our understanding of fundamental cosmic principles.
In conclusion, the assertion that the universe is slowing down raises profound questions about our current models and theories. The findings from Yonsei University could pave the way for new avenues of research in cosmology, inviting scientists to rethink long-standing assumptions about the cosmos and its future trajectory.
-

 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks agoInventor Achieves Breakthrough with 2 Billion FPS Laser Video
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoCommunity Unites for 7th Annual Into the Light Walk for Mental Health
-

 Top Stories4 weeks ago
Top Stories4 weeks agoCharlie Sheen’s New Romance: ‘Glowing’ with Younger Partner
-

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoDua Lipa Aces GCSE Spanish, Sparks Super Bowl Buzz with Fans
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoTyler Technologies Set to Reveal Q3 Earnings on October 22
-

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoMother Fights to Reunite with Children After Kidnapping in New Drama
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoCurium Group, PeptiDream, and PDRadiopharma Launch Key Cancer Trial
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoR&B Icon D’Angelo Dies at 51, Leaving Lasting Legacy
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoNorth Carolina’s Biotech Boom: Billions Invested in Manufacturing
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoNorth Carolina’s Biotech Boom: Billions in New Investments
-

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoRed Sox’s Bregman to Become Free Agent; Tigers Commit to Skubal
-

 Top Stories3 weeks ago
Top Stories3 weeks agoFormer Mozilla CMO Launches AI-Driven Cannabis Cocktail Brand Fast